Deployment
Overview

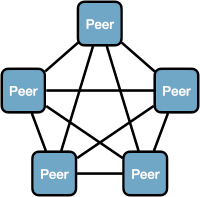
Peer to peer
By default Zenoh applications are configured to communicate peer to peer (peer mode). All applications in the local network directly communicate with each other.
Configuration
{
mode: "peer",
}
Scouting
Zenoh applications in peer mode run both multicast and gossip scouting to discover other applications or Zenoh routers and connect them.
Multicast scouting
Zenoh applications in peer mode join multicast group 224.0.0.224 on UDP port 7446 and send scout messages on this address to discover local applications and routers. They automatically connect to all accessible peer mode applications and routers they discover. The scouting address and behavior can be configured.
Configuration
{
mode: "peer",
scouting: {
multicast: {
enabled: true,
address: "224.0.0.224:7446",
interface: "auto",
autoconnect: { router: [], peer: ["router", "peer"] },
listen: true,
},
},
}
Gossip scouting
Zenoh applications in peer mode forward all local applications and routers that they already discovered to newly scouted applications. This is useful when multicast communications are not available. But applications need to connect first to an entry point to discover the rest of the system. This entry point is typically one or several Zenoh routers but can also be one or several other peers. Those entry points are configured through the connect section of the configuration.
Configuration
{
mode: "peer",
connect: {
endpoints: ["tcp/192.168.1.1:7447", "tcp/192.168.1.2:7447"],
},
scouting: {
gossip: {
enabled: true,
multihop: false,
autoconnect: { router: [], peer: ["router", "peer"] },
},
},
}
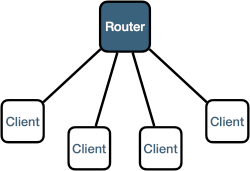
Client
Communicating peer to peer implies establishing multiple sessions with multiple other peers and maintaining a state for those sessions. Maintaining such states can be undesirable for scalability reasons or because the application runs on a constrained device. In this case the Zenoh application can be configured to operate in client mode. In this mode, the application will maintain, at any given time, a single session with another process (typically a Zenoh router) that will grant it connectivity with the rest of the system.
Configuration
{
mode: "client",
}
Scouting
Zenoh applications in client mode run multicast scouting to discover Zenoh routers and connect to them. In addition, the endpoints of one or several routers can be configured in the connect section.
Configuration
{
mode: "client",
connect: {
endpoints: ["tcp/192.168.1.1:7447", "tcp/192.168.1.2:7447"],
},
}
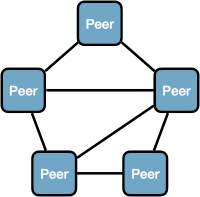
Peers mesh
In a mesh network, applications cannot directly connect to each other. Peer to peer and brokered communications may be impossible or undesirable. Zenoh applications in peer mode can run a linkstate protocol that allow them to communicate in a mesh network.
Configuration
{
mode: "peer",
routing: {
peer: {
mode: "linkstate",
},
},
}
Note: if a Zenoh router is used to connect a local mesh of Zenoh peers to a wider network, this router also needs to be configured with the same routing section.
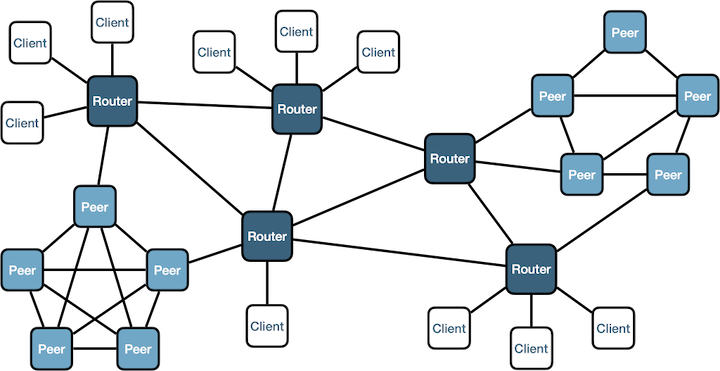
Zenoh router
Zenoh routers route data between clients and local subnetworks of peers. They can be deployed using any topology. They, by default, never try to interconnect themself automatically and must be configured with the endpoints of the other routers they are supposed to connect to.
{
connect: {
endpoints: ["tcp/192.168.1.1:7447", "tcp/192.168.1.2:7447"],
},
}
